What is Varicose Vein
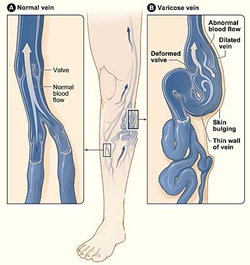
The varicose vein consists of: – A. Venous insufficiency or venous reflux at groin B. Prominent and dilated perforators. C. Dilated tortuous side branches.
Varicose vein of legs is common, affecting 1-15% of adult men and 20-25% of adult women. The leg vein normally contains multiple valves which help the blood flow in direction of the heart.When these vein valves are weakened or damaged, they are not able to pump blood towards heart and lead to blood to accumulate and pool within the leg veins. This causes swelling of the legs, aching or throbbing pain, a feeling of heaviness, tiredness, skin pigmentation, irritation or itching, and the veins become dilated and tortuous. If left untreated, the condition can worsen over time and may lead to the formation of stubborn, non-healing ulcers on the legs. Ultimately, the person is forced to lead a disabled life.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Comfortable and sedentary lifestyle, modern fashion, special postures adopted while performing professional duties have contributed to increased incidence of a set of diseases unheard of in the past. 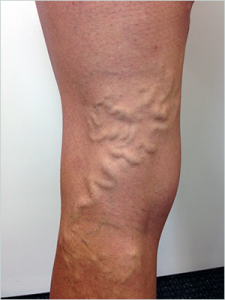 Varicose vein disease is one of them and is a direct result of sedentary lifestyle. The problem has become very common during these days. According to one estimate, 15 to 20 percent of the population in India is suffering from varicose vein disease these days. Women suffer from this disease four times more than men. There is an increased risk of the development of varicose vein among young females who wear tight jeans and high-heeled sandals.
Varicose vein disease is one of them and is a direct result of sedentary lifestyle. The problem has become very common during these days. According to one estimate, 15 to 20 percent of the population in India is suffering from varicose vein disease these days. Women suffer from this disease four times more than men. There is an increased risk of the development of varicose vein among young females who wear tight jeans and high-heeled sandals.
- The most common presenting with symptoms:
- Pain on & off.
- Swelling more prominent at the end of the day.
- Heaviness in leg.
- Fatigue.
- Prominent & dilated veins in leg veins.
- Pigmentation.
- Venous ulcer
The causes
The important causative factors are obesity, lack of exercise, abnormal pressure on veins during pregnancy, prolonged standing and prolonged sitting with legs down.The most common causes are due to advanced age, overweight and lack of exercise of legs.
Moreover, the increase in the number of persons experiencing varicose veins today is due to their profession or occupation, where the person has to constantly stand or sit for long periods with little or no movement of the legs. Computer professionals, receptionists, security guards, traffic policemen, salesmen working at counters in shops and departmental stores and persons doing desk jobs day in and day out are the worst sufferers of varicose veins.
Are women more susceptible to varicose veins?
Among females, due to some hormonal influences vein valves weaken, making them stretched, enlarged, and dilated. Additionally, during pregnancy, the increased pressure exerted on the leg veins further weakens them, often leading to varicose veins. Lifestyle choices and fashion trends also play a major role in worsening the condition. Wearing high heels, tight belts, or restrictive undergarments can obstruct smooth blood circulation in the veins, thereby contributing to the onset and progression of varicose veins.
Side effects & complications
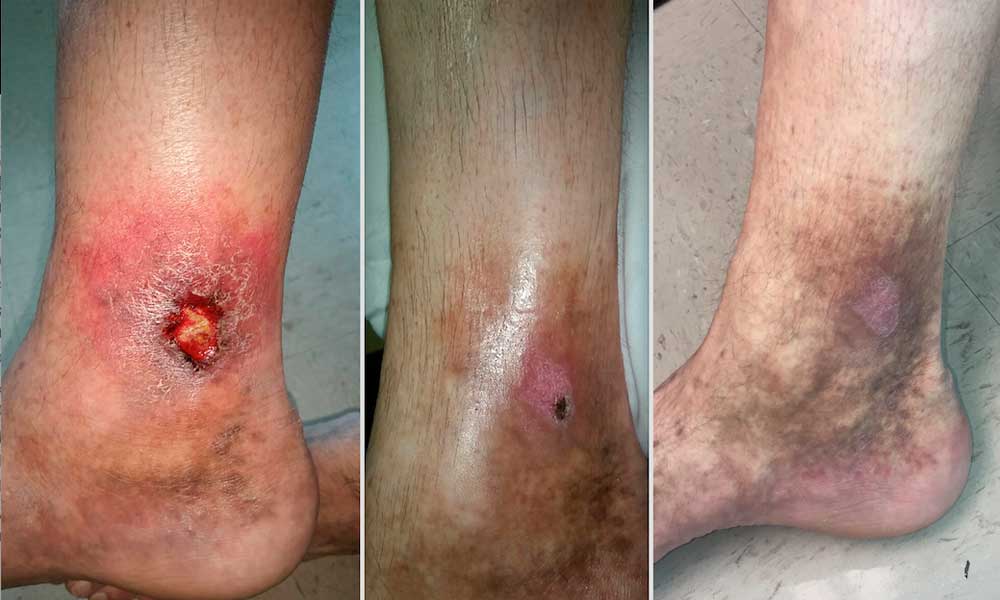
Bleeding from Superficial Veins – due to hight pressure after long standing, small weak spots may form that start to bleed through very small openings, often no bigger than a pinhole. These bleeds are most commonly seen around the ankle region; however, spontaneous bleeding can occur at any site where venous pressure remains elevated.
Venous pigmentation, also known as Hemosiderin staining of the skin is a relatively common late complication of untreated superficial chronic venous hypertension.
Venous stasis dermatitis, also known as venous eczema, is a common inflammatory skin disease that occurs on the lower extremities in patients with severe chronic venous congestion. It can arise as discrete patches or affect the leg all the way around the ankle. Symptoms of this condition include swelling (typically concentrated around the legs or ankles), changes in skin color and texture, and pain. The affected skin is itchy & irritated, showing discolouration that may appear red, purple, or even brown.
Venous stasis ulcers is the most serious complication of untreated superficial venous insufficiency and chronic venous congestion.
Superficial venous thrombosis is a blood clot, or thrombus, which develops in a vein close to the surface of the skin. The blood clot commonly appears as a red streak along the course of an affected vein, which may feel warm and tender or swollen due to inflammation (phlebitis).
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) – occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins the leg. This occurs due to slow flow in the veins. Total occlusion of one or more of the major leg veins and the impaired blood return to the heart results in massive leg swelling.
Pulmonary embolism – blood clot formed in the deep veins of the body some time migrate to lungs causing pulmonary edema. It may even lead to death if not treated immediately.
Treatment options for Varicose Veins
- Non-surgical treatment by RFA (radiofrequency ablation or laser)
- Conservative Treatment: – Elevating and flexing your legs can help reduce leg swelling and relieve other symptoms.
- Compression Stockings: – It is a specially designed elastic garments that apply gentle pressure on the veins, helping improve circulation and preventing excess blood from flowing backward. You may need to wear compression stockings only on day time.
- Sclerotherapy: – This is only for short segment disease.
- Vein Stripping Surgery: – It is a major surgery. Physician disconnects and ties off all major varicose vein branches associated with the saphenous vein, he then removes the saphenous vein and varicose veins from your leg surgically. The recurrence rate is too high and it leaves ugly scars. It needs 2-3 weeks for recovery.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Varicose Veins – Radio-frequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the latest and most effective, patient-friendly and non-surgical treatment for varicose vein using Multipolar RFA machine. Under color-doppler ultrasound vision, a radiofrequency catheter is inserted into the abnormal vein and the vessel is treated with radio-energy, resulting in closure of the involved vein.
The interventional radiologists are uniquely skilled in using the vascular system to deliver targeted treatments throughout the body without surgery. He accesses the abnormal saphenous vein just above ankle or below the knee percutaneously through a small cannula in abnormal vein. Ablation uses a thin, flexible tube called a catheter with tiny electrodes at the tip of the catheter, which heat the walls of the varicose vein, and collapses the thick veins.
Advantages of Treatment with RFA
- It is less risky as compared to surgery.
- No surgical scar on skin.
- Procedure is done under short/local anesthesia.
- It is done as daycare or 24 hrs hospital stay.
- Patients can resume normal activities within a day.
- The recurrence rate is very low as compared to surgery.