Smokers are at a Greater Risk of PAD – Stents can treat the Condition.
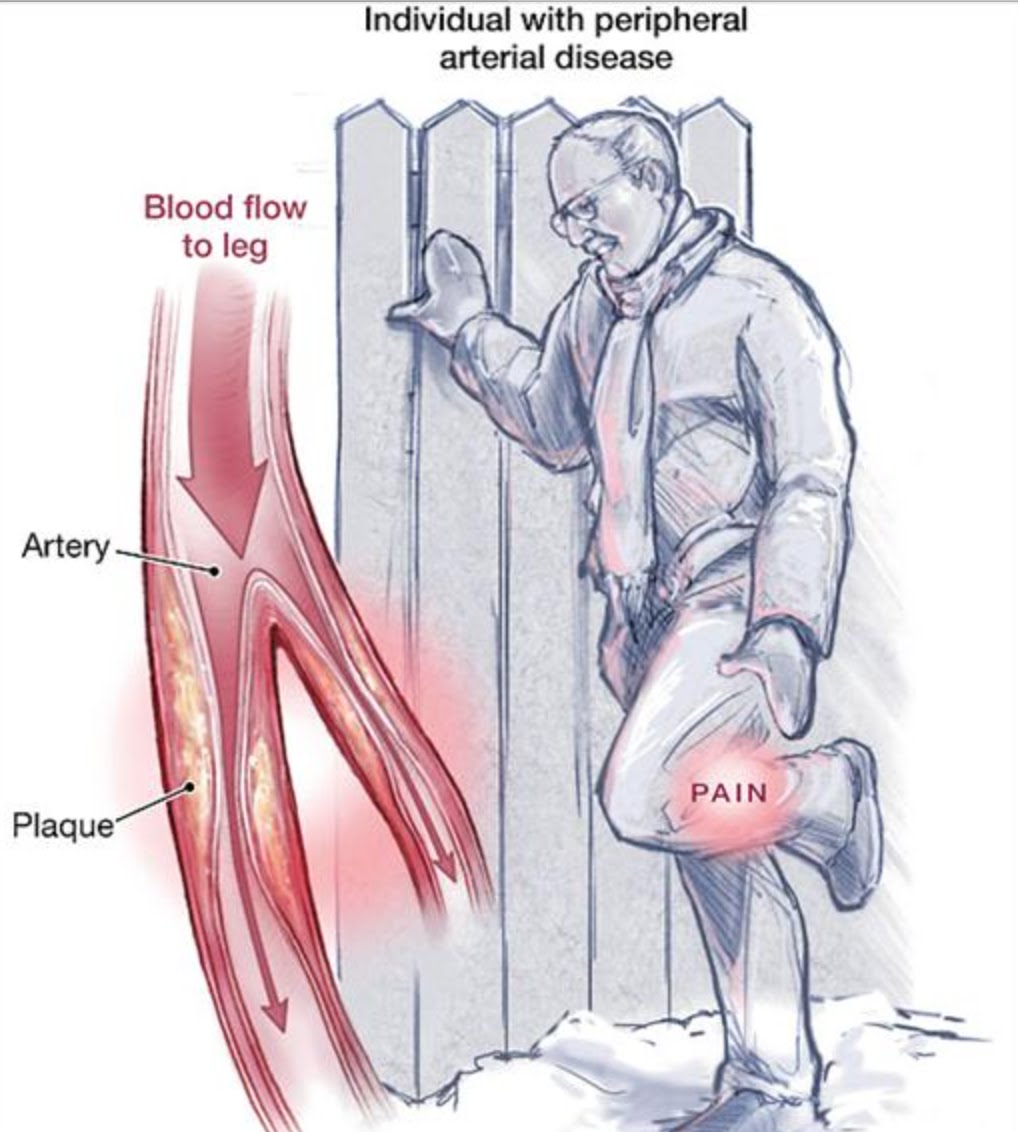
Peripheral artery disease is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. The legs don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with the demand of day to day walking. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking called claudication which disappears after a few minutes of rest but again pain starts when a person starts walking.
Peripheral artery disease symptoms include:
- Painful cramping in hip, thigh or calf muscles after certain activities, such as walking or climbing stairs (claudication)
- Leg numbness or weakness
- Coldness in lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side
- Sores on toes, feet or legs that won’t heal
- A change in the color of legs
- Hair loss or slower hair growth on feet and legs
- Slower growth of toenails
- Shiny skin on legs
- No pulse or a weak pulse in legs or feet
- Erectile dysfunction in men
If peripheral artery disease progresses, pain may occur even at rest or when lying down (ischemic rest pain). It may be intense enough to disrupt the sleep.
Causes
Atherosclerosis – fatty deposits (plaques) build up in the artery walls, thereby narrowing the lumen and reducing blood flow.
Less commonly, the cause of peripheral artery disease may be blood vessel inflammation, injury to the limb, unusual anatomy of ligaments or muscles pressing on the artery, or radiation exposure.
Factors that increase the risk of developing peripheral artery disease include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity (a body mass index over 30)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- A family history of peripheral artery disease, heart disease or stroke
- High levels of homocysteine, a protein component that helps build and maintain tissue
People who smoke or have diabetes have the greatest risk of developing peripheral artery disease
Complications
- Critical limb ischemia. This condition begins as open sores that don’t heal, an injury, or an infection of the foot or leg that progress and cause tissue death (gangrene), sometimes requiring amputation of the affected limb.
- Stroke and heart attack. Atherosclerosis that causes the signs and symptoms of peripheral artery disease can also build up in arteries supplying the heart and brain.
Prevention by Lifestyle changes
- Stop smoking.
- Supervised exercise program helping your body use oxygen more efficiently.
- Eat a healthy diet. Eating less saturated fat and adding more fruits and vegetables to your diet can help control your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which contribute to atherosclerosis.
- Avoid certain cold medications. Over-the-counter cold remedies that contain pseudoephedrine, constrict your blood vessels and may increase your PAD symptoms.
- Careful foot care – People who also have diabetes, are at risk of poor healing of sores on the lower legs and feet. and increases the risk of infection. Inspect your feet daily for injuries.
- Raise the head of your bed by 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 centimeters), because keeping your legs below the level of your heart usually lessens pain.
- Avoid cold temperatures as much as possible. Be sure to dress in warm layers.
Diagnosis –
- Physical exam. a weak or absent pulse below a narrowed area of your artery, whooshing sounds (bruits) over your arteries that can be heard with a stethoscope, evidence of poor wound healing in the area where your blood flow is restricted, and decreased blood pressure in your affected limb.
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI). It compares the blood pressure in your ankle with the blood pressure in your arm.
- Doppler ultrasound evaluates the blood flow through the blood vessels and identifies blocked or narrowed arteries.
- By injecting a dye (contrast material) into the blood vessels, the doctor can view blood flow through the arteries as it happens, using imaging techniques, such as X-ray imaging (intravenous angiography). or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) or computerized tomography angiography (CTA).
- Catheter angiography is a more invasive procedure that involves guiding a catheter through an artery in the groin to the affected area and injecting the dye. Although minimally invasive, this type of angiography gives the best visualization and allows for simultaneous diagnosis and treatment — finding the narrowed area of a blood vessel and then widening it with a dilating procedure or administering medication to improve blood flow.
Treatment
- Medicines to prevent blood clots so as to improve blood flow, to lower blood pressure (target is under 130/80 mm Hg), to lower cholesterol to less than 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and to control pain and other symptoms by using vasodilators
- Thrombolytic therapy. If there is a blood clot blocking an artery, the doctor may inject a clot-dissolving drug into your artery at the point of the clot to break it up.
- Bypass surgery. Done in case of a long segment of blocked or narrowed artery. A graft bypass is created using a vessel from another part of the body or a blood vessel made of synthetic fabric
Non-surgical Treatment using stent to open the block –
This is most commonly performed treatment option in case of short segment block. In this procedure, a small catheter is threaded through a blood vessel to the affected artery where, a small balloon on the tip of the catheter is inflated to reopen the artery and flatten the blockage into the artery wall, while at the same time stretching the artery open to increase blood flow. Then a stent is inserted in the artery to help keep it open.
Best Treatment Option- Non-surgical treatment using stent to open the block.
Advantages of Interventional Non-surgical Treatment
- It is less risky as compared to surgery
- It is cheaper than traditional surgery.
- No surgical scar on skin.
- Procedure done under local anaesthesia.
- It is done as an outpatient (OPD) / day care or short hospital stay.
- Patients can resume normal activities within a day.
- It can fast relieve pain and suffering for many cancer patients
Its safety has been proven over many years in thousands of people
Dr. Pradeep Muley is trained in the USA and Singapore and has performed over 20,000 non-surgical treatments for various diseases like uterine fibroids, uterine adenomyosis, un-operable liver tumor, liver abscesses, varicose vein, brain aneurysm and vomiting of blood from lungs and stomach. He runs the VARICOSE VEIN AND FIBROID CLINIC AT FORTIS HOSPITAL, VASANT KUNJ, NEW DELHI & created INDIA’S 1ST UTERINE FIBROID CLUB. He has treated the maximum number of fibroid patients in India through the innovative Uterine Artery Embolization method.
For more in-depth information on various non-surgical treatments available-
Mail Us: muleypradeep@hotmail.com or Visit to Website: – www.indianinterventionalradiology.com
Phone or Whatsapp: +91-9810492778
